Automated and transparent token distribution
Foster trust with Streamflow token vesting
Automate and secure your token vesting with Streamflow for seamless, transparent, and efficient distribution.








Trusted by 5000+ projects
Easy automation
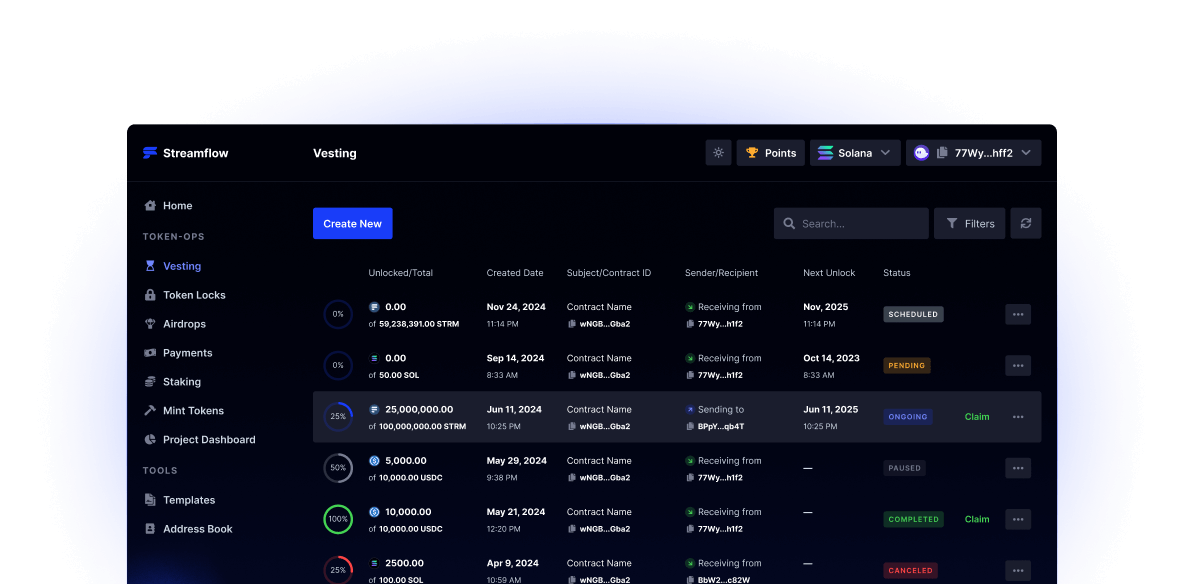
Save time and reduce manual errors in your vesting process. With our batch payment creation feature, set up vesting contracts for all your recipients in one efficient sitting. Tokens are automatically transferred to recipients' wallets upon unlocking.
Automate token unlocks
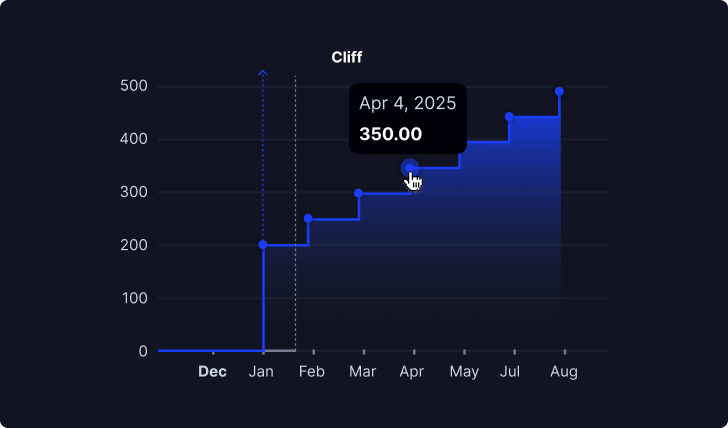
Set cliff dates with ease
Bulk import recipients
Tailored vesting
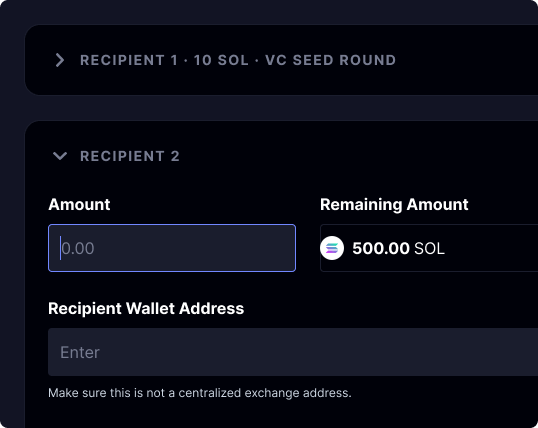
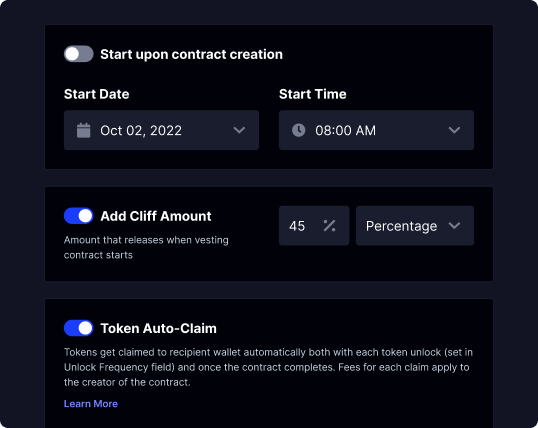
Choose how and when to pay recipients, tailoring the vesting schedule to your project's specific needs. Protect your tokens with secure on-chain management, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or fraud.
Flexible token distribution timing
Set up linear, graded or cliff vesting schedule
Transfer or cancel contracts
Token vesting transparency
Provide a centralized view of all token vesting and lock contracts, enhancing transparency for your community and investors. All on-chain transactions are visible via Blockchain Explorers, ensuring transparency and building trust with your recipients.
Enterprise-level customer?
Enterprise customers can enjoy lower fees and priority support from our team.
Schedule a call with for a custom fee offer.
Leading the way
Our platforms reliability and efficiency have earned us the trust of the biggest names in the field.

















Streamflow includes an email notification feature that informs recipients at each unlock stage, keeping them engaged and informed throughout the vesting period.
Streamflow provides flexible payment options, allowing you to choose how and when to pay recipients. You can schedule token distributions on a weekly, hourly, or even minute-by-minute basis, tailoring the vesting schedule to your project's specific needs.
We don't charge token % fees for our solutions. The fee for creating, vesting, payments or token lock contract is 0.09 SOL. Feel free to schedule a call with one of our sales representatives for additional information.